


Next: 13 Known bugs
Up: Inferring patterns of migration
Previous: 11 Unsampled subpopulations
Contents
The eigenvalue variance effective size determining the
asymptotic rate of convergence of a subdivided population is
determined by eigenvalue of the transition matrix in the
recurrence equation for the variances and covariances
rearragned into 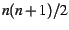 column vectors. For details, see
Tufto and Hindar (2002). The function effectpop
returns the effective size based on this approach and takes
two arguments: a migration matrix
column vectors. For details, see
Tufto and Hindar (2002). The function effectpop
returns the effective size based on this approach and takes
two arguments: a migration matrix 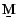 and a vector of
effective population sizes of each subpopulations. For
example, the effective size of population with migration
following a stepping stone pattern can be computed as
follows:
and a vector of
effective population sizes of each subpopulations. For
example, the effective size of population with migration
following a stepping stone pattern can be computed as
follows:
> M <- steppingstone(c(0,.1),n=4)
> M
[,1] [,2] [,3] [,4]
[1,] 0.95 0.05 0.00 0.00
[2,] 0.05 0.90 0.05 0.00
[3,] 0.00 0.05 0.90 0.05
[4,] 0.00 0.00 0.05 0.95
> N <- rep(100,4)
> N
[1] 100 100 100 100
> effectpop(M,N)
[1] 413.0410
Jarle Tufto
2001-08-28